

So, ReadyBoost only comes into action when a performance improvement is possible. When it comes to sequential operations, SuperFetch uses the files on the hard drive instead. Now, there is catch, the cache so created is used only in the case of non-sequential operations. It copies data to the cache file stored in the USB drive’s root folder.
How to use usb device for ready boost windows#
Supertech works with ReadyBoost to speed up Windows and decides what things should go into ReadyBoost cache on your USB drive and eventually into the RAM. Also, the drive’s mechanical arm does contribute to degraded performance. Thus, using ReadyBoost can be an advantage if your system is low on RAM. Mostly, SuperFetch creates a temporary cache on the main memory itself. For instance, if Chrome is the first application you use when you start your PC, SuperFetch will load Chrome files on the RAM and reduce the launch time. SuperFetch runs some algorithms to analyze your habits and automatically loads the relevant data to the main memory (RAM). However, a precursor called PreFetcher existed on Windows XP. It is another goodie which came with Windows Vista.

The real driving force behind it is SuperFetch – a disk cache management system in Windows that speeds up your system.
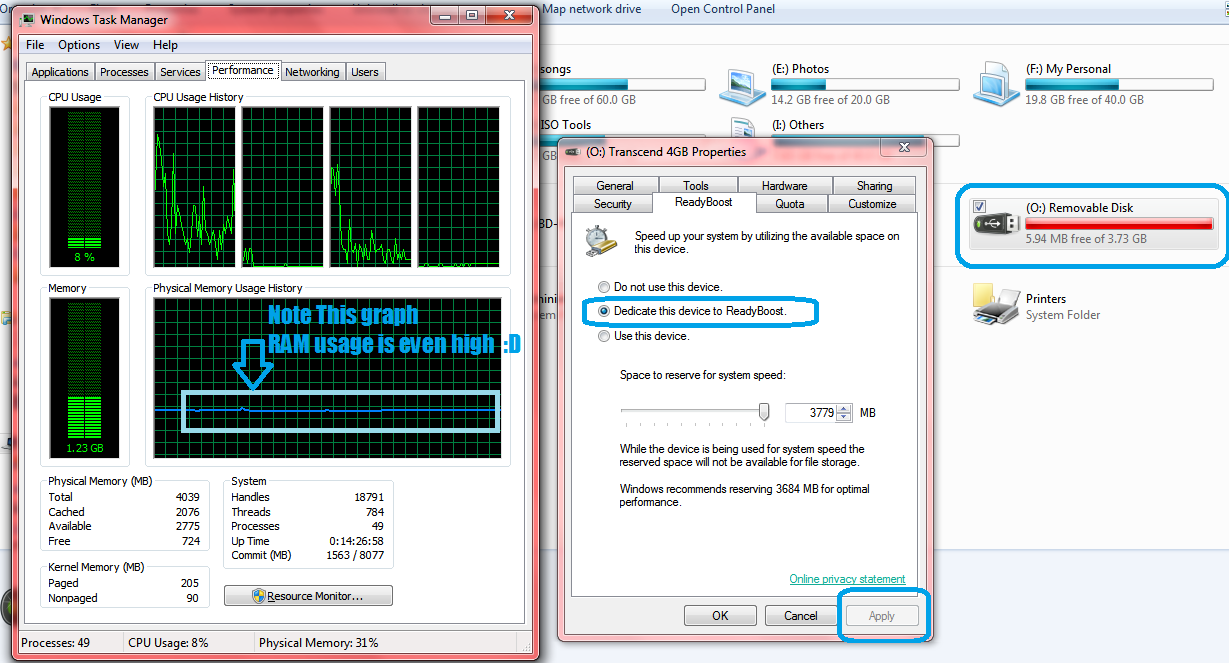
Now, ReadyBoost is a feature that allows the system to store required data in an external media for some time.
How to use usb device for ready boost how to#
Also Read: How To Use SD Card As Internal Storage On Android | Adoptable Storage On Android How ReadyBoost works? You won’t be able to speed up Windows using ReadyBoost on machines having faster hard drives. The problem has continued to lessen in the case of modern magnetic drives which are faster and run at around 7,200 RPM or above. Thus, hard drives are faster when performing sequential data reads but lag behind flash drives while performing non-sequential data read operations. That’s because the hard drives read data using a mechanical arm which is not the case of the flash drive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
